Table Of Contents
Testing for Leaks
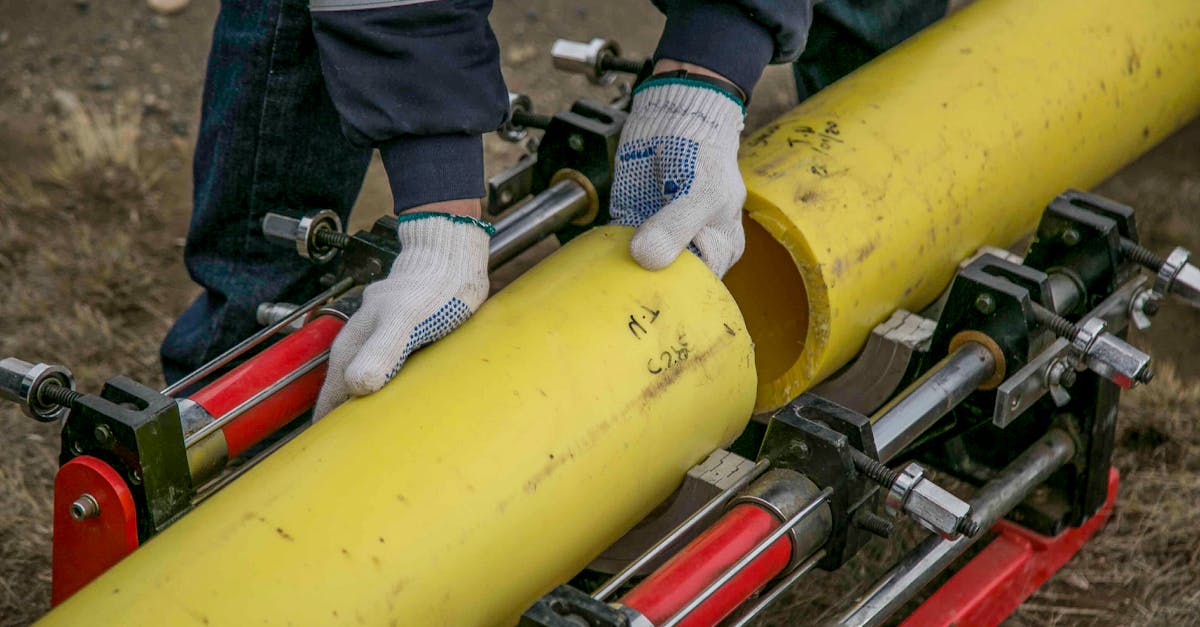
Testing for leaks is a critical step in ensuring the integrity and safety of pipe installation and repair. Various methods, such as hydrostatic testing and pneumatic testing, are commonly employed to identify leaks. Hydrostatic testing involves filling the pipe with water and pressurising it to detect any drops in pressure. This technique is effective for most types of piping systems, providing a clear indication of any weak points. Pneumatic testing, on the other hand, uses air or inert gas, requiring caution due to the potential hazards associated with compressed gas.
Leak detection techniques can also include the use of electronic leak detection systems and tracer gas methods. Electronic systems can identify even the smallest leaks by detecting variations in electrical resistance within the piping material. Tracer gas, often comprising a combination of hydrogen and nitrogen, enables the identification of leaks by monitoring gas emissions from the pipe. Employing these advanced tools enhances the reliability of testing procedures, contributing to the overall success of pipe installation and repair projects.
Techniques and Tools for Leak Detection
Various techniques and tools are employed to detect leaks in pipe installations. One common method involves using acoustic leak detection equipment, which listens for the sounds of leaking water. This tool can pinpoint the location of leaks by analysing the frequencies produced, allowing for precise identification without extensive digging or disruption. Additional methods include thermal imaging, which detects changes in temperature associated with leaks, and pressure testing, where pressure is applied to the system to identify drops that may indicate leaks.
In the context of pipe installation and repair, it’s crucial to select the appropriate leak detection method based on the specific material and conditions of the pipes. For instance, some techniques are more effective with metallic pipes, while others work better with plastic or composite materials. Regular training on these tools ensures that technicians can efficiently perform leak detection, helping to minimise potential damage and maintain system integrity.
MaterialSpecific Testing
Different materials used in pipe installations require tailored testing approaches to ensure they meet safety and performance standards. For instance, PVC pipes may undergo pressure testing to verify joint integrity while metallic pipes often require non-destructive testing methods to detect corrosion or weld defects. Understanding the specific properties of each material can influence the selection of appropriate testing techniques.
Additionally, the frequency and type of material-specific testing depend on the application environment and regulatory demands. For example, pipes used in underground installations may need to pass rigorous tests for durability and resistance to external forces. Pipe installation and repair practices must include these material considerations to achieve long-lasting and compliant outcomes, ultimately ensuring public safety and system reliability.
Requirements for Different Types of Pipes
The requirements for testing and inspecting different types of pipes can vary based on the material used and the intended application. For instance, metallic pipes often require more rigorous checks for signs of corrosion or fatigue, while plastic pipes demand attention to their joining methods and overall integrity. Each material poses unique challenges that must be evaluated to ensure reliability and safety, especially in high-pressure applications. Pipe installation and repair processes should always adhere to the established standards for the materials in use.
When dealing with various pipe types, it is crucial to follow industry-specific guidelines that outline the necessary tests and inspection methods. For example, copper piping systems undergo pressure testing to verify they meet installation specifications. In contrast, sewer and drain pipes are tested for leak resistance through air or water tests to confirm their effectiveness. Regular assessments of pipe installation and repair projects help maintain compliance with regulatory standards and assure system longevity.
Frequency of Inspections
The frequency of inspections for pipe installation and repair is crucial to maintaining system integrity and performance. Regular inspection schedules allow for timely identification of potential issues, helping to mitigate risks associated with leaks and structural failures. Industry standards often dictate that new installations undergo more frequent checks shortly after completion to ensure all components are functioning correctly and meet safety requirements. As time goes on, the intervals can be adjusted based on the condition of the infrastructure and any historical data regarding its performance.
Several factors influence the timing of these inspections, including the materials used in the pipes, the environment in which they are installed, and the specific operational demands placed on the system. For instance, pipes subject to extreme pressures or corrosive substances may necessitate more rigorous and frequent inspections than those in less demanding conditions. Additionally, regulations and compliance standards can impose mandatory inspection timelines that must be adhered to, ensuring that pipe installation and repair practices consistently meet safety and quality benchmarks.
Factors Influencing Inspection Timelines
Inspection timelines can vary significantly based on several key factors. The age and condition of the existing infrastructure often play a crucial role. Older pipes may require more frequent inspections due to their susceptibility to wear and tear. Additionally, the environmental conditions surrounding the installation site, such as soil type and moisture levels, can impact the deterioration rates of pipes, necessitating adjusted inspection schedules.
Moreover, the type of pipe installation and repair being undertaken influences how inspections are timed. For example, installations made with modern materials may require less frequent checks compared to traditional systems made from older materials. Regulatory guidelines may also dictate when inspections should take place, adding another layer of complexity. Understanding these factors is essential for effective maintenance and ensuring the longevity of pipe systems.
FAQS
What is the primary purpose of inspecting and testing pipe installations?
The primary purpose is to ensure the integrity, safety, and functionality of the piping system, which helps prevent leaks and potential hazards.
What are the common techniques used for leak detection in pipes?
Common techniques include pressure testing, ultrasonic testing, dye testing, and using acoustic sensors to identify leaks.
Are there different testing requirements for various types of pipes?
Yes, testing requirements can vary significantly depending on the material of the pipes, such as PVC, copper, or steel, and the specific application they are used for.
How often should pipe installations be inspected?
The frequency of inspections can depend on several factors, including the type of pipe, environmental conditions, and regulatory requirements, but regular inspections are generally recommended to ensure ongoing safety and performance.
What factors influence the timelines for inspecting pipe installations?
Factors that influence inspection timelines include the age of the installation, the environment in which the pipes are located, any past issues with leaks or failures, and any regulatory or industry standards that apply.